3D printing is no longer just an experimental trend. It is becoming an essential tool in industries and daily life.
The keyword here is transformation—because 3D printing is reshaping how things are made and who can make them. This article explains the technology and shows how it will impact every part of the modern world.
What is 3D Printing Technology?
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing. It builds objects by adding material layer by layer, rather than cutting away from a solid block.
Definition and Core Concepts
Understanding 3D printing starts with knowing how it differs from traditional production. Additive manufacturing adds only what is needed, while older methods subtract or mold.
There are three primary types of 3D printers: FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), SLA (Stereolithography), and SLS (Selective Laser Sintering).
Each uses different materials and methods, but the core idea is the same—you create things by building them from nothing.
How Does it Work?
To print an object, you begin with a digital 3D model. That model is converted into layers using the slicer software. Then, the printer reads the layers and prints each one in sequence.
Common materials include plastics, resins, and metals. Some printers also use biocompatible materials for medical use. The process is fast, flexible, and gets more affordable every year.
Industries Transformed by 3D Printing
3D printing is not limited to one field. Its ability to customize, prototype, and scale solutions is changing industries around the globe.
Healthcare and Medical Applications
Healthcare is one of the most impacted areas. Custom prosthetics and orthopedic implants are now printed to fit the individual.
Doctors use printed surgical models to prepare for complex procedures. In bioprinting, researchers are printing tissues and organ-like structures.
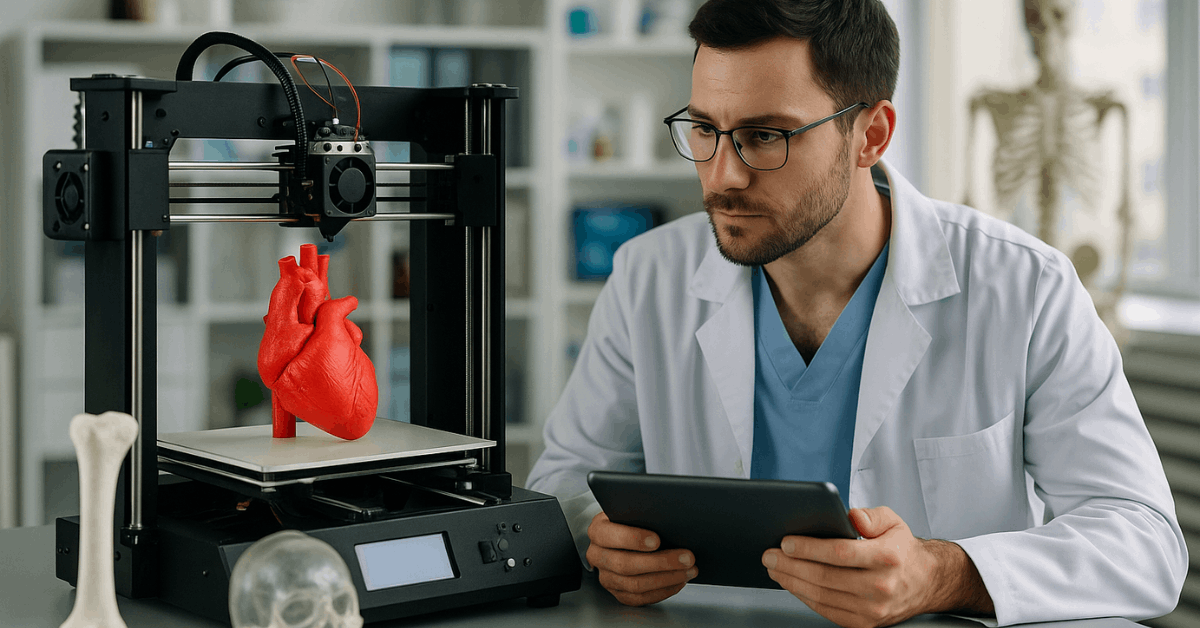

This helps reduce reliance on donors and improves transplant readiness. Personalized medicine is no longer a dream.
Construction and Housing
3D-printed houses are being tested in many countries. The process builds walls using cement or similar material. These structures can be completed in a few days with minimal labor.
It dramatically reduces waste and material costs. Affordable housing is more achievable through this method. It also supports disaster relief housing in emergency zones.
Aerospace and Automotive
In aerospace, 3D-printed parts are valued for being lightweight and strong. This helps improve fuel efficiency. Custom parts are also easier and cheaper to produce.
In automotive, rapid prototyping speeds up design and testing. Even full car parts are now being printed. Companies like SpaceX and BMW are already applying this technology.
Education and Research
Educational institutions use 3D printing for hands-on learning. Students in engineering, art, and medicine all benefit. Prototypes, models, and simulations help explain complex concepts.
3D printing also encourages problem-solving and creativity. Universities use it for research in materials and product testing. It makes high-level research more accessible.
Consumer Products and Retail
Retail is shifting to on-demand production. Consumers can design or customize their products online. Fashion, shoes, jewelry, and even home items are created just for you.
It reduces the need for mass inventory. Waste and storage costs go down. This also supports local production and small businesses.
Economic and Business Impacts
3D printing isn’t just technical; it shifts how businesses operate. From supply chains to job roles, the effects are deep.
Disruption of Supply Chains
Traditional manufacturing relies on centralized factories and long shipping chains. 3D printing allows production to happen anywhere.
This cuts lead times and costs. It also makes businesses more flexible in a crisis. Customization and local delivery become possible. Products no longer need to sit in warehouses for months.
Job Creation and Job Shifts
This technology changes the type of jobs that exist. There is demand for CAD designers, machine operators, and maintenance technicians.
Some traditional roles may shrink, especially in assembly. However, new fields emerge, such as 3D modeling and printer management. Education must adapt to teach these skills.
Startup Opportunities and Entrepreneurship
You don’t need a factory to create a product anymore. Entrepreneurs can design, prototype, and sell from a small space. Platforms like Etsy and Kickstarter are filled with 3D-printed items.
It lowers the cost of starting a business. Designers get direct access to customers. This decentralizes innovation and empowers small players.
Environmental Benefits
Besides business, 3D printing offers clear environmental advantages. It reduces waste and energy use while promoting sustainability.
Waste Reduction
Traditional manufacturing often cuts away excess material. 3D printing uses only what is needed.
This means minimal waste. Materials like recyclable plastic and bio-resins are common. It’s possible to use scrap material for new prints. This helps close the loop in the production cycle.
Energy Efficiency
3D printing consumes less energy compared to many conventional methods. Local production reduces transportation costs.
Digital designs mean fewer errors and reworks. This helps conserve fuel and electricity. Sustainability becomes part of the business model.
Sustainable Design and Circular Economy
You can repair products instead of replacing them. Parts can be printed when needed. This supports the idea of a circular economy.
People can keep using and fixing what they own. It also reduces pressure on natural resources.
Social and Humanitarian Impact
3D printing doesn’t just benefit big companies. It supports people in vulnerable communities.
Empowering Developing Countries
Local 3D printers can solve local problems. Medical tools, farming equipment, and learning aids can be produced on-site.
This avoids long delays in delivery. Rural and remote areas gain new capabilities. Small businesses emerge in places previously left out. The economic empowerment is real.
Disaster Relief and Emergency Response
3D printing plays a big role in emergencies. Relief workers can print shelters, tools, and medical parts directly on-site. It shortens response time.
In conflict zones or after natural disasters, access to resources becomes immediate. Designs can be shared digitally. Only the raw material needs to be shipped.
Challenges and Ethical Questions
As with any powerful tool, 3D printing comes with its challenges. These must be managed responsibly.
Intellectual Property and Legal Issues
Anyone can download and print designs. This raises concerns about copyright and patents. Products may be copied and sold illegally.
Enforcing IP laws becomes harder. This can discourage innovation. Legal systems are still catching up.
Regulatory Hurdles
Not all 3D-printed products are safe. There must be standards and quality checks. Medical or aviation parts need strict regulation.
Governments must create rules without slowing progress. This is especially important for cross-border sales. Different countries may follow different safety rules.
Accessibility and Digital Divide
3D printing requires access to hardware, software, and skills. Not all regions or people have this access. The risk is that the technology helps only a few.
We must ensure inclusive access and education. Otherwise, the benefits will remain limited to tech-savvy areas.
The Future of 3D Printing
The journey is far from over. The next decade will bring even more changes.
Bioprinting and Organ Fabrication
Researchers are working on printing tissues, cartilage, and organs. Bioprinters place living cells in layers. These structures can grow and function like real tissue.
The future could include on-demand organs for surgery. This may solve donor shortages. It will change medicine forever.
4D Printing and Smart Materials
4D printing adds a new layer. Printed objects respond to time, temperature, or moisture. They bend or reshape when conditions change.
This has uses in medicine, wearables, and robotics. It makes products smarter and more adaptable. It also reduces manual work.
Integration with AI and Robotics
Artificial intelligence helps optimize designs for strength, weight, and function. AI also improves printer speed and accuracy.
Robotics can automate the entire printing process. From design to delivery, everything can be handled by machines. This allows 24/7 production with minimal errors.
A World Rebuilt, Layer by Layer
3D printing is changing how the world creates, repairs, and innovates. Its effects are already visible in medicine, construction, business, and education.
The potential of this technology will only grow as it becomes more accessible. If you stay informed and engaged, you can be part of the transformation, not just a spectator.



